Throughout the year, people often use terms like equinox and solstice. Some even celebrate the summer solstice or send well wishes for the occasion, similar to other popular celebrations. But what are the definitions and distinctions between a solstice and an equinox?
Let’s begin with the equinox.
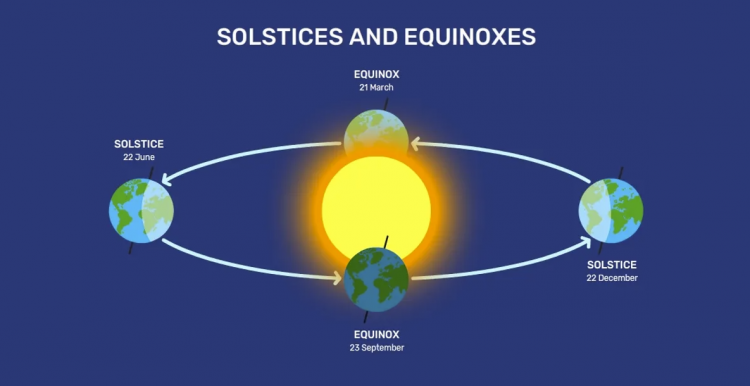
During the equinoxes, which happen in March and September, the sun is precisely positioned above the equator at noon. It is worth noting that in the Northern Hemisphere, March signifies the arrival of spring, while in the Southern Hemisphere, it heralds the onset of fall or autumn.
The March equinox is commonly referred to as the vernal equinox or the spring equinox. The term “equinox” is derived from the Latin words “aequus” (equal) and “nox” (night), signifying a balance between day and night. Due to the Earth’s axial tilt and its changing orientation towards the Sun, there is a specific time when the lengths of day and night are approximately equal. This occurs when the sun is positioned on the celestial equator. Depending on your distance from the equator, you can expect to have approximately 12 hours of daylight and 12 hours of night.
Since these equinoxes are measurable astronomical events that happen annually, they can be accurately predicted down to the minute. According to NASA, the March equinox is set to occur at 11:06 pm EDT on March 19, or 3:06 p.m. UTC on March 20 in 2024.
Now let’s discuss the solstice
The solstice happens twice a year: once in winter and once in summer. Based on scientific data, the Met Office states that the occurrence of the former takes place approximately on June 21 in the Northern Hemisphere, while the latter, the winter solstice, happens around December 21.
During the summer solstice, the sun reaches its peak height for the year, while during the winter solstice, it reaches its lowest point. During this period of the year, the sun’s path is at its maximum distance from the equator, according to Britannica. This occurs when the planet’s poles are either tilted significantly towards or away from the Sun.
The angle at which Earth is tilted on its axis, approximately 23.5 degrees, is a crucial factor in determining the occurrence of solstices. During the summer solstice, the Northern Hemisphere experiences an extended period of daylight due to its tilt towards the Sun. This phenomenon is particularly pronounced in certain regions, like the Arctic Circle, where sunlight can persist for a full 24 hours. It is worth noting that the winter solstice marks the shortest day of the year, while the summer solstice signifies the longest day of the year.
Another way to define solstices is by solar declination, which refers to the latitude on Earth where the sun is directly overhead at noon. The solar declination is the angle formed by the sun’s rays and the equatorial plane. During the summer solstice, the solar declination is approximately 23.5°N at the Tropic of Cancer. According to National Geographic, the solar declination is around 23.5°S at the Tropic of Capricorn in December.
 Tech Gadget Central Latest Tech News and Reviews
Tech Gadget Central Latest Tech News and Reviews